Architecture Overview
This section provides a conceptual overview of Eko’s architecture. While the implementation details may vary, understanding these core principles will help you effectively build and maintain Eko-based automation.
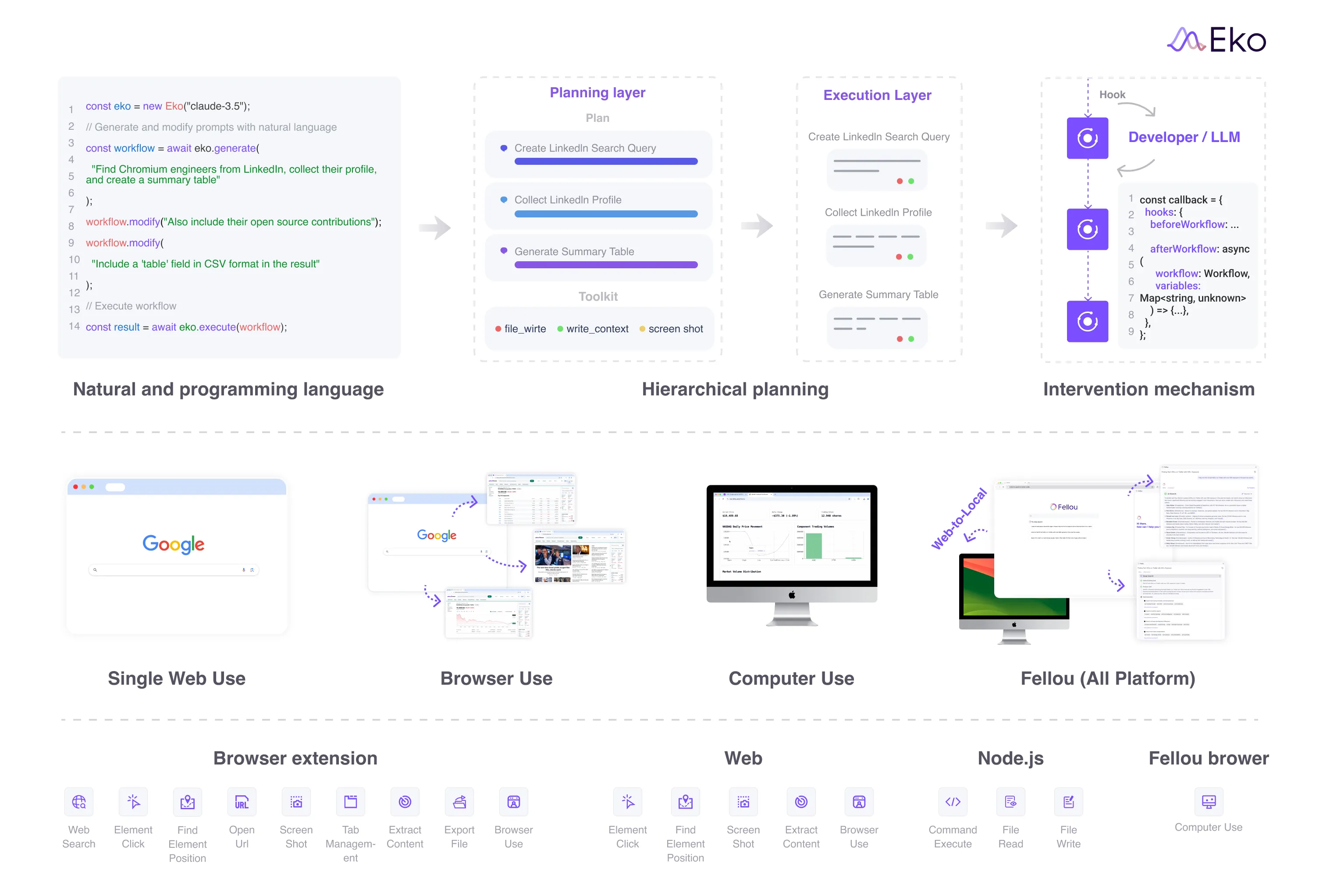
Hierarchical Planning
At the heart of Eko is a hierarchical planning framework that separates task planning from execution:
Planning Layer (eko.generate)
- Converts natural language descriptions into structured workflows
- Uses LLMs (Claude/OpenAI) to break down complex tasks into discrete steps
- Validates workflow structure and tool requirements before execution
- Creates reusable, inspectable workflow definitions
Execution Layer (eko.execute)
- Dynamically executes workflows while adapting to runtime conditions
- Handles tool selection and sequencing based on context
- Manages dependencies between workflow nodes
- Provides hook-based execution control

Learn more in Hierarchical Planning.
Web Information Extraction
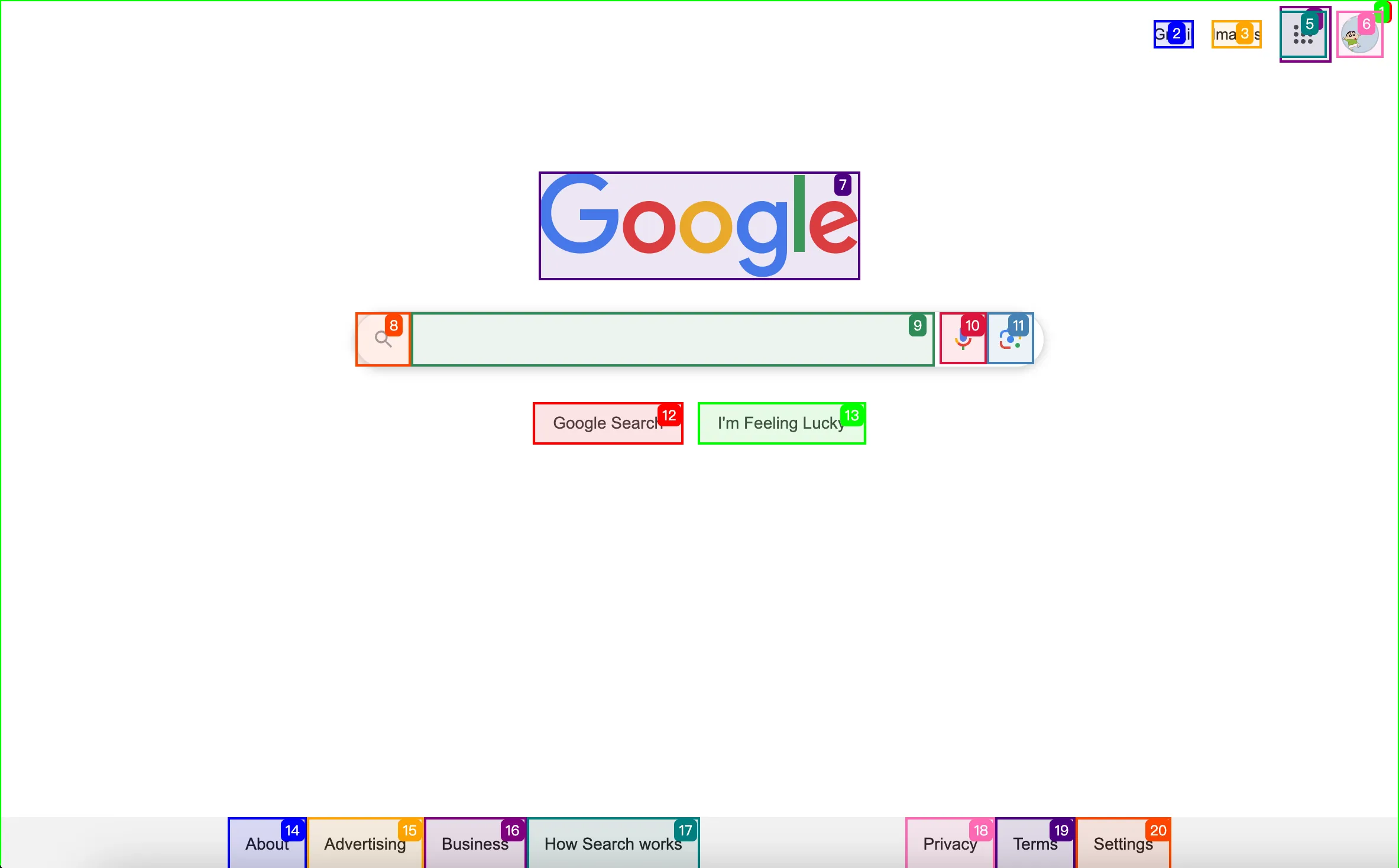 Eko employs an innovative approach to web information through:
Eko employs an innovative approach to web information through:
- Identifies and tags interactive elements on web pages with unique IDs
- Creates visual overlays showing element relationships
- Combines screenshots with pseudo-HTML for robust element identification
- Enhances accuracy of browser automation through combined visual and structural understanding
This technology is particularly important for browser automation tasks, providing reliable element identification across different page states. Learn more in Web Information Extraction.
Environment-Aware Architecture
Eko provides consistent capabilities across different JavaScript environments while adapting to each environment’s unique constraints:
Browser Extension Environment
- Full browser automation capabilities
- Tab and window management
- DOM interaction and content extraction
- Cross-origin communication handling
Web Environment
- Sandboxed operation for web applications
- DOM manipulation and event handling
- Content extraction and processing
- Secure API endpoint integration
Node.js Environment
- System-level file operations
- Command execution and process management
- Full access to Node.js APIs
- Direct access to local resources
See Environment-Aware Architecture for details on how Eko adapts to each environment.
Tool System
Tools are the building blocks of automation in Eko:
Tool Definition
- Each tool has a unique name and description
- Defines its input schema and requirements
- Implements specific execution logic
- Can access shared execution context
Tool Registration
- Manages available tools for each environment
- Handles tool registration and validation
- Provides tool enumeration and metadata
- Ensures tool compatibility
Tool Categories
- Browser automation tools (OpenUrl, BrowserUse, etc.)
- System interaction tools (FileRead, CommandExecute, etc.)
- Content processing tools (ExtractContent, ExportFile, etc.)
- Custom tool support for extensibility
Learn more in the documentation on Tools Overview.
Hook System
Hooks provide deep visibility and control over workflow execution:
Workflow Hooks
- beforeWorkflow/afterWorkflow for setup and cleanup
- Access to workflow-level state and variables
- Control over workflow initialization and completion
Subtask Hooks
- beforeSubtask/afterSubtask for node-level control
- Monitor and modify subtask execution
- Access to execution context and results
Tools Hook
- beforeToolUse/afterToolUse for fine-grained control
- Modify tool inputs and outputs
- Implement custom error handling and recovery
Learn more in Hook System.
Next Steps
- Understand how workflows are structured in Workflow Structure
- Learn about browser automation in Web Extraction Technology
- Explore tool development in Tools Overview
- Master execution control with the Hook System